目录
当掌握了 Python 基础以后,接下来我们进入爬虫的学习,我将详细讲解Python爬虫的各个方面,从基础到进阶,包括如何处理动态内容、反爬虫策略等,通过多个实例来帮助理解。
网络爬虫深度解析
什么是网络爬虫?
网络爬虫(Web Crawler)是一种自动浏览互联网并收集数据的程序,也称为网络蜘蛛(Web Spider),是一种自动化程序,专门用于在互联网上系统地浏览网页并收集信息。想象一下:
-
图书馆管理员: 爬虫就像在巨大的互联网图书馆中帮你查找特定书籍的管理员
-
数据收集员: 自动从成千上万个网页中提取你需要的信息
-
数字探险家: 在互联网的海洋中探索并带回有价值的数据宝藏
爬虫的工作原理详解
爬虫工作遵循"请求-响应-解析-存储"的循环流程。首先向目标服务器发送HTTP请求,接收返回的HTML响应,然后解析文档结构提取目标数据,最后清洗整理并存储。整个过程涉及URL管理、内容去重、反爬应对等多个技术环节的协同工作。
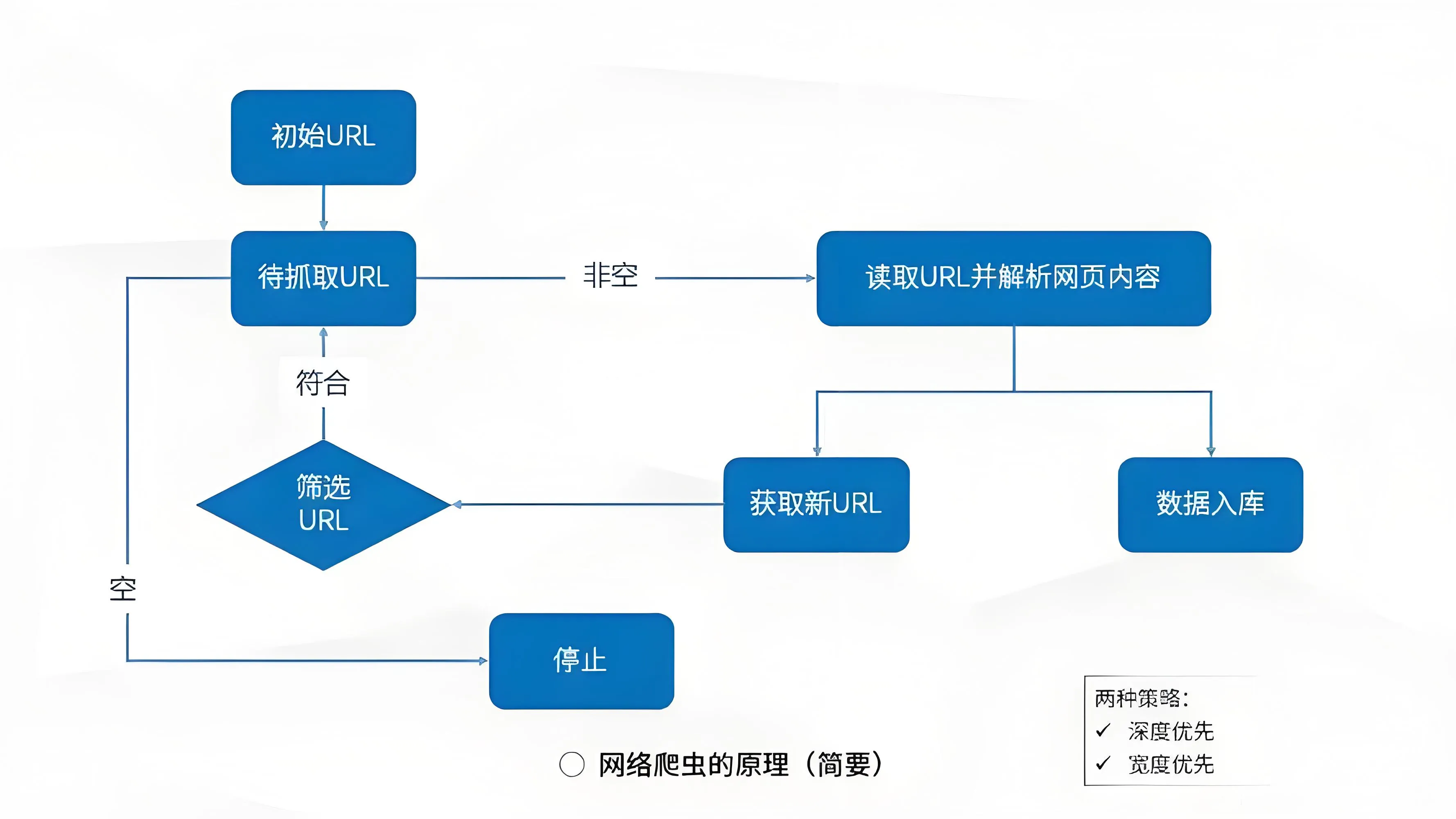
详细工作流程:
发送请求 → 获取响应 → 解析内容 → 提取数据 → 存储数据(循环直到完成所有目标页面)
- URL管理:维护一个待爬取URL队列
- HTTP请求:向目标服务器发送请求
- 响应处理:接收服务器返回的HTML、JSON等数据
- 内容解析:从响应中提取有用信息
- 数据清洗:清理和格式化提取的数据
- 存储入库:将数据保存到文件或数据库
- URL去重:避免重复爬取相同页面
爬虫的应用场景
爬虫技术广泛应用于搜索引擎索引、价格监控、舆情分析、学术研究等领域。电商平台用它追踪竞争对手价格,新闻机构用它聚合多方资讯,研究人员用它收集实验数据,企业用它监控品牌声誉,几乎任何需要从网络获取数据的场景都能见到爬虫的身影。
-
搜索引擎:Google、百度等搜索引擎的核心技术
-
价格监控:电商平台价格比较和趋势分析
-
新闻聚合:自动收集多个新闻源的内容
-
社交媒体分析:分析用户行为和趋势
-
学术研究:收集实验数据和研究资料
-
竞争情报:监控竞争对手的动态
Python 爬虫实战
环境搭建与工具准备
在开始以前,检查环境是否安装完成
bash# 检查Python是否安装
python --version
# 或
python3 --version
# 如果没有安装,从官网下载:https://www.python.org/downloads/
必需库的安装和说明:
requests库负责发送HTTP请求,beautifulsoup4用于解析HTML文档,lxml提供更快的解析性能。可选安装selenium处理动态网页,aiohttp实现异步爬取,pandas进行数据处理。这些库共同构成了Python爬虫的技术生态体系。
bash# 核心请求库 - 用于发送HTTP请求
pip install requests
# HTML解析库 - 用于解析和提取HTML中的数据
pip install beautifulsoup4
# 高性能解析器 - 比默认解析器更快
pip install lxml
# 可选:处理动态网页
pip install selenium
# 可选:异步爬虫
pip install aiohttp
# 可选:数据处理
pip install pandas
HTTP协议基础:爬虫的通信语言
Http,超文本传输协议,是一个基于请求与响应,无状态的,应用层的协议,常基于TCP/IP协议传输数据,互联网上应用最为广泛的一种网络协议,所有的WWW文件都必须遵守这个标准。
Http的传输:
- 长链接: 建立连接 -> 传输数据 -> 《过程持续连接》 -> 传输数据 -> 关闭连接
- 短链接: 建立连接 -> 传输数据 -> 关闭连接... 发起请求 ... 建立连接 -> 传输数据 -> 关闭连接
Http三次握手与四次挥手:
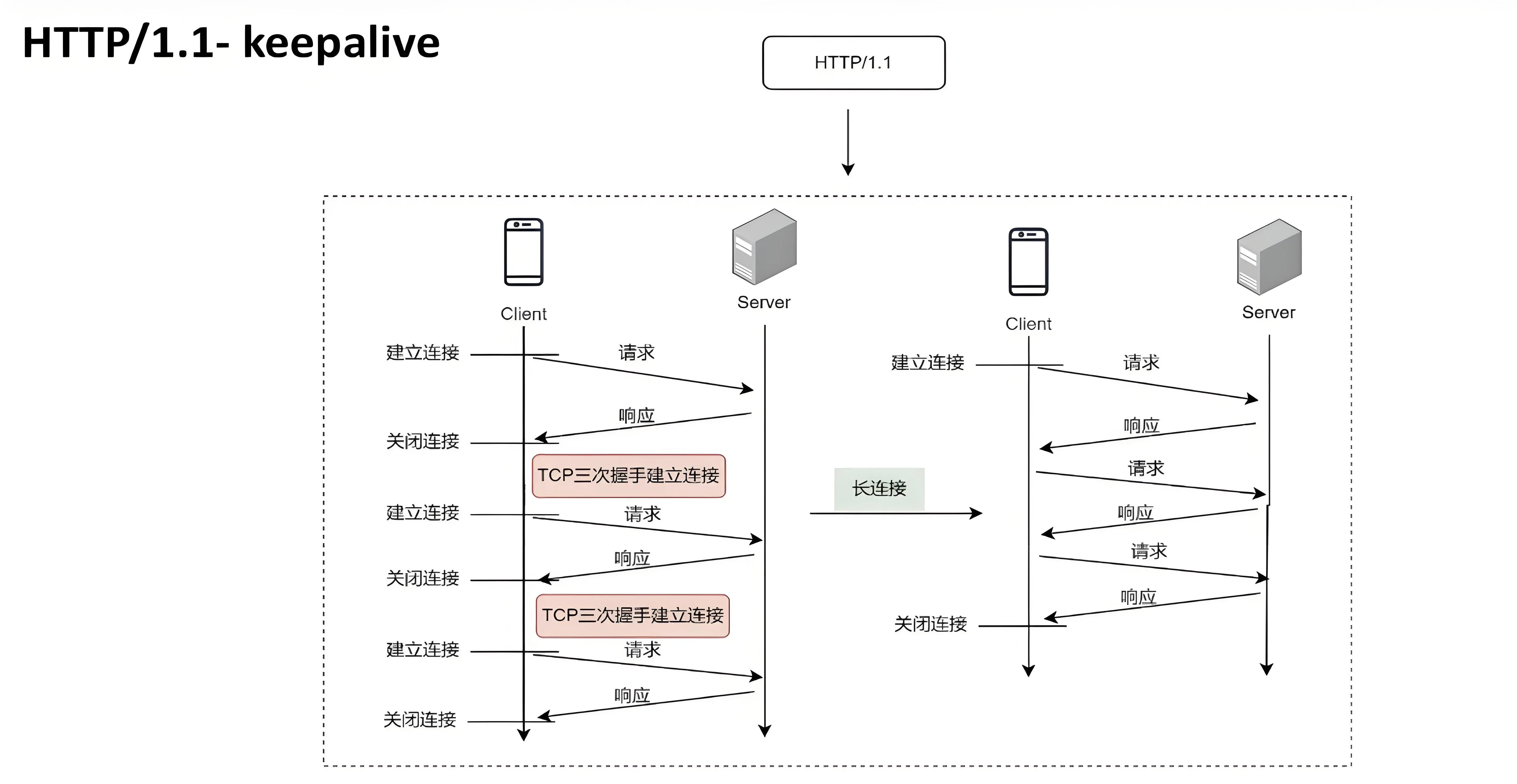
HTTP请求详解
完整的HTTP请求包含URL、方法、请求头和请求体。爬虫需要合理设置User-Agent模拟浏览器,管理Cookie维持会话状态,处理重定向和超时。精细化的请求配置能够提高爬虫的成功率和稳定性。
pythonimport requests
# 一个完整的HTTP请求包含以下部分
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36',
'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en-US;q=0.5,en;q=0.3',
'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests': '1',
}
cookies = {
'session_id': 'abc123',
'user_preference': 'dark_mode'
}
# 发送GET请求
response = requests.get(
'https://httpbin.org/get',
headers
)
提示
此处使用模块 'requests' 的软件包,也可直接使用 Python 内置的 urllib 库替代 requests 库
pythonimport urllib.request
import urllib.parse
import json
# 一个完整的HTTP请求包含以下部分
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36',
'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en-US;q=0.5,en;q=0.3',
'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests': '1',
}
cookies = {
'session_id': 'abc123',
'user_preference': 'dark_mode'
}
# 构造请求
url = 'https://httpbin.org/get'
req = urllib.request.Request(url, None, headers)
# 发送GET请求
try:
response = urllib.request.urlopen(req)
data = response.read().decode('utf-8')
print(data)
except Exception as e:
print(f"请求失败: {e}")
HTTP状态码含义
状态码是服务器对请求的响应状态标识。200表示成功,301/302是重定向,404页面不存在,403访问被拒,500服务器错误。爬虫需要根据不同的状态码采取相应处理策略,确保程序的健壮性。
python# 常见的HTTP状态码
status_codes = {
200: '成功 - 请求成功处理',
301: '永久重定向',
302: '临时重定向',
400: '错误请求 - 服务器不理解请求',
403: '禁止访问 - 服务器拒绝请求',
404: '未找到 - 请求的资源不存在',
500: '服务器内部错误',
503: '服务不可用 - 服务器过载或维护'
}
def handle_response(response):
"""处理不同的HTTP响应状态"""
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.text
elif response.status_code == 404:
print("页面不存在")
return None
elif response.status_code == 403:
print("访问被拒绝,可能需要登录或验证")
return None
elif response.status_code == 500:
print("服务器错误")
return None
else:
print(f"未知错误,状态码: {response.status_code}")
return None
BeautifulSoup深度解析
BeautifulSoup 是Python最流行的HTML解析库,提供直观的API来遍历和搜索文档树。它支持多种解析器,能处理格式混乱的HTML,通过标签名、类名、ID等选择器精准定位目标元素,大大简化数据提取过程。
选择器详解
BeautifulSoup 提供了多种灵活的方式来解析和提取 HTML/XML 数据。为了让你能快速上手,下面这个表格汇总了它的主要方法、参数含义和调用方式。
| 方法/属性 | 主要参数 | 关键参数说明 | 调用示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
find_all() | name, attrs, recursive, text, limit | name:按标签名查找(字符串、正则、列表、函数)。 attrs:按属性查找(字典)。 recursive:是否递归查找子孙节点(默认True)。 text:按文本内容查找(字符串、正则、列表)。 limit:限制返回结果数量。 | soup.find_all('div', class_='item') soup.find_all(attrs={"data-foo": "value"}) |
find() | name, attrs, recursive, text | 参数同 find_all(),但只返回第一个匹配结果。 | soup.find('title') |
select() | CSS 选择器字符串 | 使用 CSS 选择器 查找,返回所有匹配的列表。 | soup.select('div.content > p') |
select_one() | CSS 选择器字符串 | 使用 CSS 选择器 查找,返回第一个匹配结果。 | soup.select_one('#login-form') |
.string | - | 获取单个标签的直接文本内容。若标签内有多个内容,可能返回 None。 | tag.string |
.get_text() | separator, strip | 获取标签及其所有子孙标签的文本,可指定分隔符和是否去除首尾空格。 | tag.get_text(' ', strip=True) |
.get() / [] | 属性名 | 获取标签的属性值。 | tag['href'] tag.get('href') |
.contents | - | 获取标签的直接子节点列表(包括字符串)。 | tag.contents |
.children | - | 获取标签的直接子节点的迭代器。 | for child in tag.children: |
.parent | - | 获取标签的直接父节点。 | tag.parent |
.next_sibling /.previous_sibling | - | 获取后一个或前一个兄弟节点(可能是换行符等字符串)。 | tag.next_sibling |
BeautifulSoup 提供 find()、find_all()、select() 等多种选择方法。可按标签名、类名、ID属性查找元素,支持CSS选择器语法,能够处理复杂的嵌套结构和属性条件。熟练掌握选择器是高效提取数据的关键技能。
pythonfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
# 示例HTML
html_doc = """
<html>
<head>
<title>示例网页</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="main-content">
<h1 class="title">欢迎来到我的网站</h1>
<div class="article">
<h2>文章标题1</h2>
<p class="content">这是第一篇文章的内容。</p>
<span class="date">2023-10-01</span>
</div>
<div class="article">
<h2>文章标题2</h2>
<p class="content">这是第二篇文章的内容。</p>
<span class="date">2023-10-02</span>
</div>
<ul class="menu">
<li><a href="/home">首页</a></li>
<li><a href="/about">关于我们</a></li>
<li><a href="/contact">联系我们</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser')
# 1. 按标签名查找
titles = soup.find_all('h2')
print("所有标题:", [title.text for title in titles])
# 2. 按类名查找
articles = soup.find_all('div', {'class': 'article'})
print("文章数量:", len(articles))
# 3. 按ID查找
main_content = soup.find('div', {'id': 'main-content'})
print("主内容区域:", main_content is not None)
# 4. 组合查找
article_titles = soup.select('div.article h2')
print("文章标题:", [title.text for title in article_titles])
# 5. 属性查找
links = soup.find_all('a', {'href': True})
print("所有链接:", [link['href'] for link in links])
# 6. 层级查找
menu_links = soup.select('ul.menu li a')
print("菜单链接:", [link.text for link in menu_links])
数据提取技巧
数据提取涉及文本获取、属性提取、结构遍历等操作。需要注意处理缺失数据、文本清洗、编码转换等问题。良好的错误处理机制和数据类型转换能够确保提取数据的完整性和准确性。
python# 继续使用上面的soup对象
# 提取文本内容
def extract_article_data(article_div):
"""从文章div中提取结构化数据"""
title = article_div.find('h2').text.strip()
content = article_div.find('p', {'class': 'content'}).text.strip()
date = article_div.find('span', {'class': 'date'}).text.strip()
return {
'title': title,
'content': content,
'date': date
}
# 应用到所有文章
articles_data = []
for article in soup.find_all('div', {'class': 'article'}):
article_data = extract_article_data(article)
articles_data.append(article_data)
print("提取的文章数据:", articles_data)
# 处理嵌套数据
def extract_nested_data():
"""处理更复杂的嵌套结构"""
all_data = {}
# 提取导航菜单
menu_items = {}
for li in soup.select('ul.menu li'):
link = li.find('a')
menu_items[link.text] = link['href']
all_data['menu'] = menu_items
# 提取文章信息
all_data['articles'] = articles_data
return all_data
nested_data = extract_nested_data()
print("完整提取的数据:", nested_data)
实战项目:完整的图书爬虫
通过构建图书信息爬虫项目,综合运用requests发送请求、BeautifulSoup解析页面、csv存储数据等技术。项目涵盖单页爬取、分页处理、异常处理等完整流程,是初学者理想的实践案例。
单页爬虫完整实现
单页爬虫聚焦于单个页面的数据提取,包括发送请求、解析HTML、提取图书标题、价格、评分等字段,并将结果存储为结构化数据。重点训练基础爬虫技能的完整应用,为复杂爬虫开发打下基础。
pythonimport requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import csv
import time
import os
from urllib.parse import urljoin
class BookScraper:
def __init__(self, base_url="http://books.toscrape.com/"):
self.base_url = base_url
self.session = requests.Session()
self.setup_session()
def setup_session(self):
"""设置会话参数"""
self.session.headers.update({
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36',
'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
})
def get_page(self, url):
"""获取页面内容,包含错误处理"""
try:
response = self.session.get(url)
response.raise_for_status() # 如果状态码不是200,抛出异常
response.encoding = 'utf-8'
return response.text
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"请求失败: {e}")
return None
def parse_book_list(self, html):
"""解析图书列表页面"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
books = []
# 查找所有图书条目
book_elements = soup.find_all('article', {'class':'product_pod'})
for book_element in book_elements:
book_info = self.extract_book_basic_info(book_element)
if book_info:
books.append(book_info)
return books
def extract_book_basic_info(self, book_element):
"""从图书元素中提取基本信息"""
try:
# 书名
title = book_element.h3.a['title']
# 价格
price_text = book_element.find('p', {'class':'price_color'}).text
price = self.clean_price(price_text)
# 评分
rating_class = book_element.find('p', {'class':'star-rating'})['class'][1]
rating = self.convert_rating(rating_class)
# 详情链接
relative_url = book_element.h3.a['href']
detail_url = urljoin(self.base_url, relative_url)
return {
'title': title,
'price': price,
'rating': rating,
'detail_url': detail_url,
'scraped_time': time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
}
except (AttributeError, KeyError, IndexError) as e:
print(f"提取图书信息时出错: {e}")
return None
def clean_price(self, price_text):
"""清理价格文本"""
# 移除货币符号和空格
return price_text.replace('£', '').strip()
def convert_rating(self, rating_class):
"""将评分等级转换为数字"""
rating_map = {
'One': 1, 'Two': 2, 'Three': 3, 'Four': 4, 'Five': 5
}
return rating_map.get(rating_class, 0)
def get_book_detail(self, detail_url):
"""获取图书详细信息"""
html = self.get_page(detail_url)
if not html:
return {}
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
detail_info = {}
try:
# 提取详细信息
product_description = soup.find('div', {'id':'product_description'})
if product_description:
detail_info['description'] = product_description.find_next_sibling('p').text.strip()
# 提取产品信息表中的数据
product_table = soup.find('table', {'class':'table table-striped'})
if product_table:
rows = product_table.find_all('tr')
for row in rows:
header = row.find('th').text.strip()
value = row.find('td').text.strip()
detail_info[header] = value
# 提取分类
breadcrumb = soup.find('ul', {'class':'breadcrumb'})
if breadcrumb:
category_links = breadcrumb.find_all('li')[2] # 第三个li元素是分类
detail_info['category'] = category_links.a.text.strip()
except Exception as e:
print(f"提取详细信息时出错: {e}")
return detail_info
def save_to_csv(self, data, filename='books.csv'):
"""保存数据到CSV文件"""
if not data:
print("没有数据可保存")
return
# 获取所有可能的字段名
fieldnames = set()
for book in data:
fieldnames.update(book.keys())
fieldnames = sorted(list(fieldnames))
with open(filename, 'w') as file:
writer = csv.DictWriter(file, fieldnames)
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerows(data)
print(f"数据已保存到 {filename},共 {len(data)} 条记录")
def main():
"""主函数"""
scraper = BookScraper()
print("开始爬取图书信息...")
# 获取首页图书列表
html = scraper.get_page(scraper.base_url)
if not html:
print("无法获取首页内容")
return
books = scraper.parse_book_list(html)
print(f"从首页找到 {len(books)} 本书")
# 为每本书获取详细信息
complete_books_data = []
for i, book in enumerate(books, 1):
print(f"正在处理第 {i}/{len(books)} 本书: {book['title']}")
# 获取详细信息
detail_info = scraper.get_book_detail(book['detail_url'])
# 合并基本信息与详细信息
complete_book = {**book, **detail_info}
complete_books_data.append(complete_book)
# 礼貌延迟
time.sleep(1)
# 保存数据
scraper.save_to_csv(complete_books_data)
print("爬取完成!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
分页爬虫增强版
分页爬虫需要处理多页面遍历,自动识别下一页链接,维护URL队列,控制请求频率。通过循环机制实现全站数据采集,涉及页面导航、链接去重、进度监控等进阶功能。
pythonclass PaginatedBookScraper(BookScraper):
def __init__(self, base_url="http://books.toscrape.com/"):
super().__init__(base_url)
self.all_books = []
def scrape_all_pages(self, max_pages=None):
"""爬取所有分页"""
page = 1
has_next_page = True
while has_next_page and (max_pages is None or page <= max_pages):
print(f"正在爬取第 {page} 页...")
if page == 1:
url = self.base_url
else:
url = f"{self.base_url}catalogue/page-{page}.html"
html = self.get_page(url)
if not html:
print(f"第 {page} 页获取失败")
break
# 检查是否是有效页面(不是404)
if "404 Not Found" in html:
print("没有更多页面了")
break
books = self.parse_book_list(html)
if not books:
print("当前页面没有找到图书")
break
self.all_books.extend(books)
print(f"第 {page} 页找到 {len(books)} 本书")
# 检查是否有下一页
has_next_page = self.check_next_page(html)
page += 1
# 礼貌延迟
time.sleep(2)
print(f"总共爬取 {len(self.all_books)} 本书")
return self.all_books
def check_next_page(self, html):
"""检查是否有下一页"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
next_button = soup.find('li', {'class':'next'})
return next_button is not None
def scrape_with_detail(self, max_pages=None):
"""爬取所有页面并获取详细信息"""
# 先获取所有图书的基本信息
self.scrape_all_pages(max_pages)
# 然后获取每本书的详细信息
complete_data = []
total_books = len(self.all_books)
for i, book in enumerate(self.all_books, 1):
print(f"获取详细信息: {i}/{total_books} - {book['title']}")
detail_info = self.get_book_detail(book['detail_url'])
complete_book = {**book, **detail_info}
complete_data.append(complete_book)
# 更长的延迟,避免对服务器造成压力
time.sleep(2)
return complete_data
# 使用分页爬虫
def run_paginated_scraper():
scraper = PaginatedBookScraper()
print("开始分页爬取...")
# 只爬取前3页作为示例
complete_data = scraper.scrape_with_detail(3)
# 保存数据
scraper.save_to_csv(complete_data, 'all_books_with_details.csv')
print("分页爬取完成!")
return complete_data
# 运行分页爬虫
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_paginated_scraper()
高级技巧与最佳实践
包括错误处理、重试机制、数据验证等进阶技术。使用会话保持连接,设置超时防止阻塞,实现指数退避重试策略。这些实践能显著提升爬虫的稳定性和 professionalism。
错误处理与重试机制
网络请求具有不确定性,需要完善的错误处理机制。通过try-except捕获异常,使用重试策略应对临时故障,设置合理的超时时间,记录详细日志便于问题排查,确保爬虫在恶劣网络环境下仍能可靠运行。
pythonimport time
from requests.adapters import HTTPAdapter
from urllib3.util.retry import Retry
class RobustScraper(BookScraper):
def __init__(self, base_url="http://books.toscrape.com/"):
super().__init__(base_url)
self.setup_robust_session()
def setup_robust_session(self):
"""设置健壮的会话,包含重试机制"""
retry_strategy = Retry(
3,
1,
None,
None,
None,
None,
None,
[429, 500, 502, 503, 504], # 需要重试的状态码
)
adapter = HTTPAdapter(10, 10, retry_strategy)
self.session.mount("http://", adapter)
self.session.mount("https://", adapter)
def robust_get_page(self, url, max_retries=3):
"""带重试机制的页面获取"""
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
response = self.session.get(url)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.text
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"请求失败 (尝试 {attempt + 1}/{max_retries}): {e}")
if attempt < max_retries - 1:
wait_time = 2 ** attempt # 指数退避
print(f"等待 {wait_time} 秒后重试...")
time.sleep(wait_time)
else:
print("所有重试尝试均失败")
return None
def safe_extract(self, element, selector, attribute=None, default=""):
"""安全地提取元素内容"""
try:
if attribute:
return element.select_one(selector)[attribute]
else:
selected = element.select_one(selector)
return selected.text.strip() if selected else default
except (AttributeError, KeyError, TypeError):
return default
数据清洗与验证
原始爬取数据往往包含噪音,需要进行清洗和验证。包括去除空白字符、标准化日期格式、验证数值范围、处理缺失值等操作。高质量的数据清洗能够提升后续数据分析的准确性和可靠性。
pythonimport re
from datetime import datetime
class DataCleaner:
@staticmethod
def clean_text(text):
"""清理文本数据"""
if not text:
return ""
# 移除多余的空格和换行
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text).strip()
# 移除不可见字符
text = ''.join(char for char in text if char.isprintable())
return text
@staticmethod
def parse_price(price_text):
"""解析价格"""
if not price_text:
return 0.0
# 提取数字部分
match = re.search(r'[\d.,]+', price_text)
if match:
price_str = match.group().replace(',', '')
try:
return float(price_str)
except ValueError:
return 0.0
return 0.0
@staticmethod
def parse_date(date_text):
"""解析日期"""
if not date_text:
return None
# 尝试多种日期格式
date_formats = [
'%Y-%m-%d',
'%d/%m/%Y',
'%m/%d/%Y',
'%B %d, %Y',
'%d %B %Y'
]
for fmt in date_formats:
try:
return datetime.strptime(date_text, fmt).date()
except ValueError:
continue
return None
@staticmethod
def validate_book_data(book_data):
"""验证图书数据的完整性"""
required_fields = ['title', 'price']
missing_fields = [field for field in required_fields if not book_data.get(field)]
if missing_fields:
print(f"警告: 缺少必要字段: {missing_fields}")
return False
# 验证价格是否为有效数字
try:
price = float(book_data['price'])
if price <= 0:
print(f"警告: 无效价格: {price}")
return False
except (ValueError, TypeError):
print("警告: 价格格式无效")
return False
return True
@staticmethod 注解
静态方法装饰器,表示该方法属于类本身而不是类的实例,可以直接通过类名调用,无需创建类的实例对象
应对反爬虫策略
网站会采用各种技术阻止爬虫访问,包括验证码、频率限制、IP封禁等。应对措施包括设置随机延迟、轮换User-Agent、使用代理IP、模拟人类行为模式等,在遵守规则的前提下完成数据采集任务。
基本的反爬虫应对
通过设置合理的请求间隔、使用真实浏览器标识、维护会话状态等基本措施规避反爬虫检测。遵循robots.txt协议,控制采集频率,避免对目标网站造成负担,体现技术伦理和责任意识。
pythonclass StealthScraper(RobustScraper):
def __init__(self, base_url="http://books.toscrape.com/"):
super().__init__(base_url)
self.setup_stealth_headers()
def setup_stealth_headers(self):
"""设置更真实的请求头"""
self.session.headers.update({
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/96.0.4664.110 Safari/537.36',
'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8',
'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate, br',
'DNT': '1',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests': '1',
'Sec-Fetch-Dest': 'document',
'Sec-Fetch-Mode': 'navigate',
'Sec-Fetch-Site': 'none',
'Cache-Control': 'max-age=0',
})
def random_delay(self, min_delay=1, max_delay=3):
"""随机延迟,模拟人类行为"""
delay = random.uniform(min_delay, max_delay)
time.sleep(delay)
def scrape_with_stealth(self, urls):
"""使用隐身模式爬取"""
results = []
for i, url in enumerate(urls, 1):
print(f"爬取进度: {i}/{len(urls)}")
html = self.robust_get_page(url)
if html:
# 解析页面...
pass
# 随机延迟
self.random_delay(2, 5)
return results
使用代理IP
代理IP能够隐藏真实访问源,避免IP被封锁。需要维护代理IP池,验证代理可用性,实现自动切换机制。高质量的代理服务是大型爬虫项目成功的关键因素之一。
pythonclass ProxyScraper(StealthScraper):
def __init__(self, base_url="http://books.toscrape.com/", proxy_list=None):
super().__init__(base_url)
self.proxy_list = proxy_list or []
self.current_proxy_index = 0
def get_next_proxy(self):
"""获取下一个代理"""
if not self.proxy_list:
return None
proxy = self.proxy_list[self.current_proxy_index]
self.current_proxy_index = (self.current_proxy_index + 1) % len(self.proxy_list)
return proxy
def get_with_proxy(self, url):
"""使用代理发送请求"""
proxy = self.get_next_proxy()
if proxy:
try:
response = self.session.get(url, proxies={'http': proxy, 'https': proxy}, timeout=10)
return response.text
except requests.exceptions.RequestException:
print(f"代理 {proxy} 失败,尝试下一个")
return self.get_with_proxy(url) # 递归尝试下一个代理
else:
return self.robust_get_page(url)
数据存储方案
爬取的数据需要持久化存储,常见格式包括CSV、JSON、数据库等。CSV适合表格数据,JSON保留层次结构,SQLite便于查询,Excel方便人工查看。根据数据特性和使用场景选择合适的存储方案。
多种存储格式
多种存储格式:不同的存储格式各有优劣。CSV简单通用,JSON保持数据结构,数据库支持复杂查询,Excel便于业务人员使用。实际项目中往往需要组合使用多种存储方式,满足不同层次的数据使用需求。
pythonimport json
import sqlite3
import pandas as pd
class DataStorage:
@staticmethod
def save_json(data, filename):
"""保存为JSON格式"""
with open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)
print(f"数据已保存为JSON: {filename}")
@staticmethod
def save_csv(data, filename):
"""保存为CSV格式"""
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.to_csv(filename, index=False, encoding='utf-8')
print(f"数据已保存为CSV: {filename}")
@staticmethod
def save_sqlite(data, db_name, table_name):
"""保存到SQLite数据库"""
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_name)
# 创建表(如果不存在)
if data:
# 使用第一行数据推断列名和类型
sample_row = data[0]
columns = []
for key, value in sample_row.items():
if isinstance(value, (int, float)):
col_type = 'REAL'
else:
col_type = 'TEXT'
columns.append(f'"{key}" {col_type}')
create_table_sql = f'''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS {table_name} (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
{", ".join(columns)}
)
'''
conn.execute(create_table_sql)
# 插入数据
for row in data:
placeholders = ', '.join(['?' for _ in row])
columns_str = ', '.join([f'"{col}"' for col in row.keys()])
sql = f'INSERT INTO {table_name} ({columns_str}) VALUES ({placeholders})'
conn.execute(sql, list(row.values()))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
print(f"数据已保存到数据库: {db_name}.{table_name}")
@staticmethod
def save_excel(data, filename):
"""保存为Excel格式"""
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.to_excel(filename, index=False)
print(f"数据已保存为Excel: {filename}")
项目结构与代码组织
推荐的项目结构
pythonbook_scraper/
│
├── src/
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── scraper.py # 主要爬虫类
│ ├── data_cleaner.py # 数据清洗
│ ├── storage.py # 数据存储
│ └── utils.py # 工具函数
│
├── data/
│ ├── raw/ # 原始数据
│ └── processed/ # 处理后的数据
│
├── logs/ # 日志文件
├── config/ # 配置文件
├── tests/ # 测试代码
├── requirements.txt # 依赖包列表
└── main.py # 主程序
配置文件示例
将URL、超时时间、数据库连接等参数提取到配置文件中,实现代码与配置分离。支持不同环境的多份配置,通过配置文件快速调整爬虫行为,提高灵活性和可维护性。
python# config/settings.py
import os
from datetime import datetime
# 基础配置
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
DATA_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'data')
LOG_DIR = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'logs')
# 爬虫配置
CRAWLER_CONFIG = {
'base_url': 'http://books.toscrape.com/',
'timeout': 10,
'max_retries': 3,
'delay_range': (1, 3), # 延迟范围(秒)
'user_agents': [
'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36',
'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36',
],
}
# 日志配置
LOG_CONFIG = {
'level': 'INFO',
'format': '%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
'filename': os.path.join(LOG_DIR, f'scraping_{datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d")}.log')
}
下一步学习路径
进阶技术栈
Scrapy提供完整的爬虫框架,异步编程提升采集效率,分布式技术处理海量数据,机器学习辅助内容解析。掌握这些进阶技术能够应对更复杂的爬虫场景和业务需求。
- Scrapy框架:专业的Python爬虫框架
pip install scrapy
-
异步爬虫:使用aiohttp提高效率
pythonimport aiohttp import asyncio -
分布式爬虫:使用Redis、Celery等
-
机器学习:用于内容分类和智能解析
职业发展方向
-
数据工程师:专注于数据采集和处理
-
爬虫工程师:专门开发维护爬虫系统
-
数据分析师:利用爬取的数据进行分析
-
机器学习工程师:为模型准备训练数据
总结
通过这份详细的教程,你应该已经掌握了:
-
爬虫基础知识:理解了HTTP协议、HTML解析
-
核心工具使用:熟练使用requests和BeautifulSoup
-
实战项目经验:完成了完整的图书爬虫项目
-
高级技巧:错误处理、反爬虫应对、数据存储
-
最佳实践:代码组织、项目结构、爬虫礼仪
记住,爬虫技术是一把双刃剑。在享受数据采集便利的同时,务必:
-
✅ 尊重网站的robots.txt
-
✅ 遵守相关法律法规
-
✅ 控制爬取频率,不影响网站正常运行
-
✅ 只爬取公开可用的数据
现在,你已经具备了编写专业爬虫程序的能力。选择一个你感兴趣的项目,开始你的爬虫之旅吧!


本文作者:柳始恭
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
